How to setup docker swarm on AWS EC2

Docker is a powerful tool for containerization; providing a lightweight and efficient way to package applications with their dependencies. Docker Swarm made deployment handy as it is easy to maintain and scale applications. I have found it intresting to setup AWS EC2 with docker. Here is the steps that I followed.
Step 1: Security group.
First we need to login into AWS Console and select select security group.
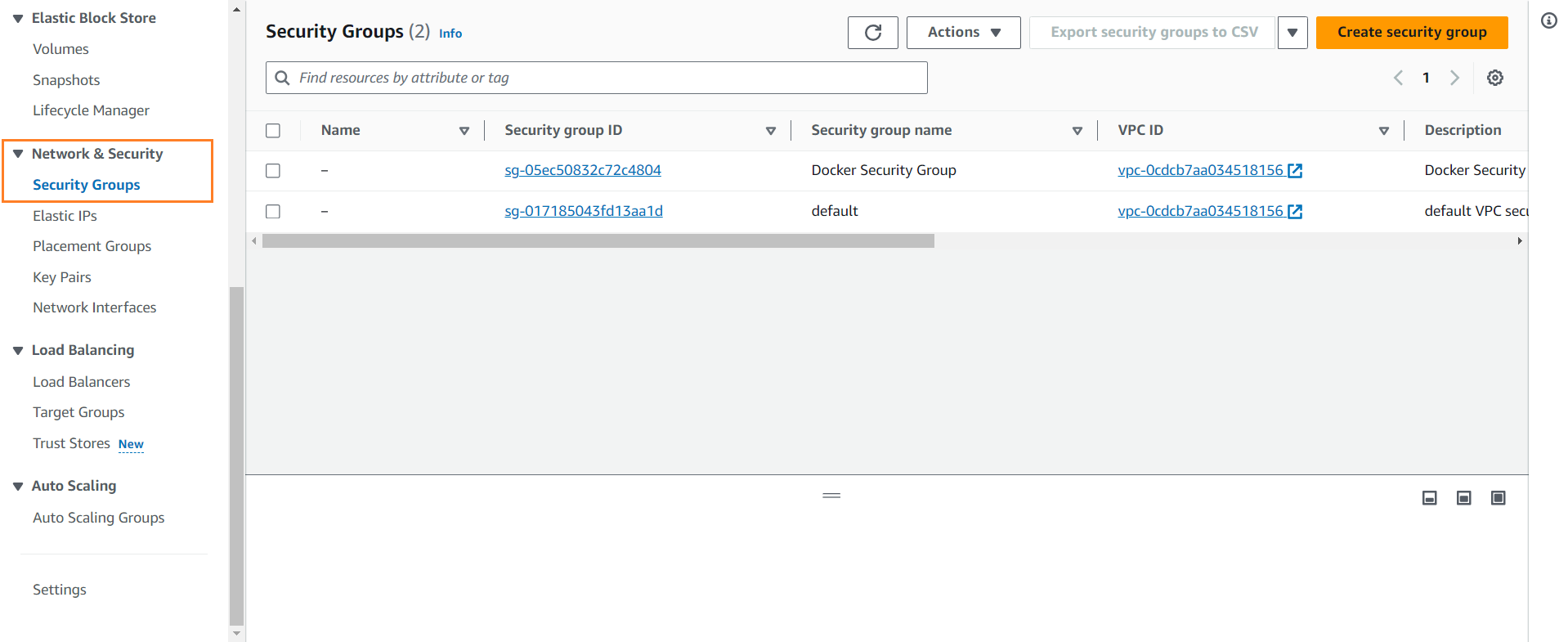
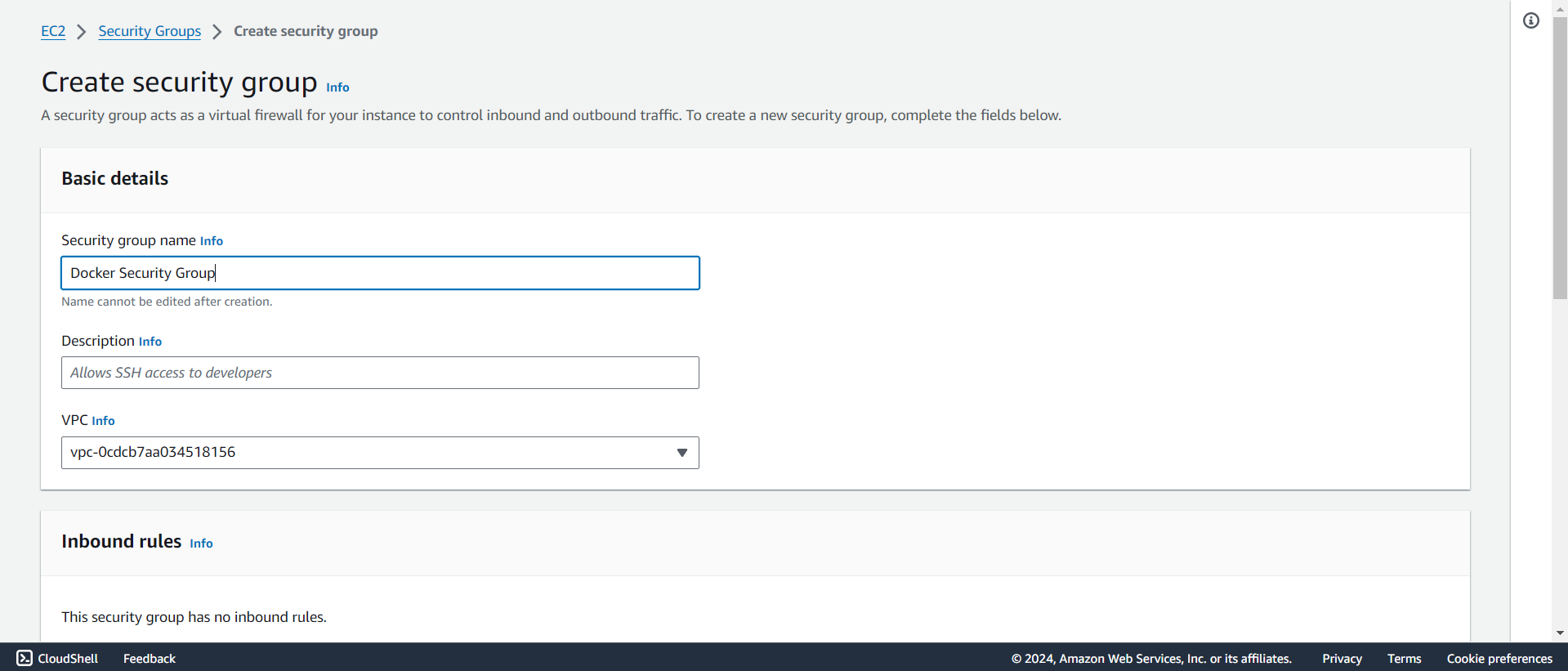
We will create a new security group to setup communication between docker nodes.
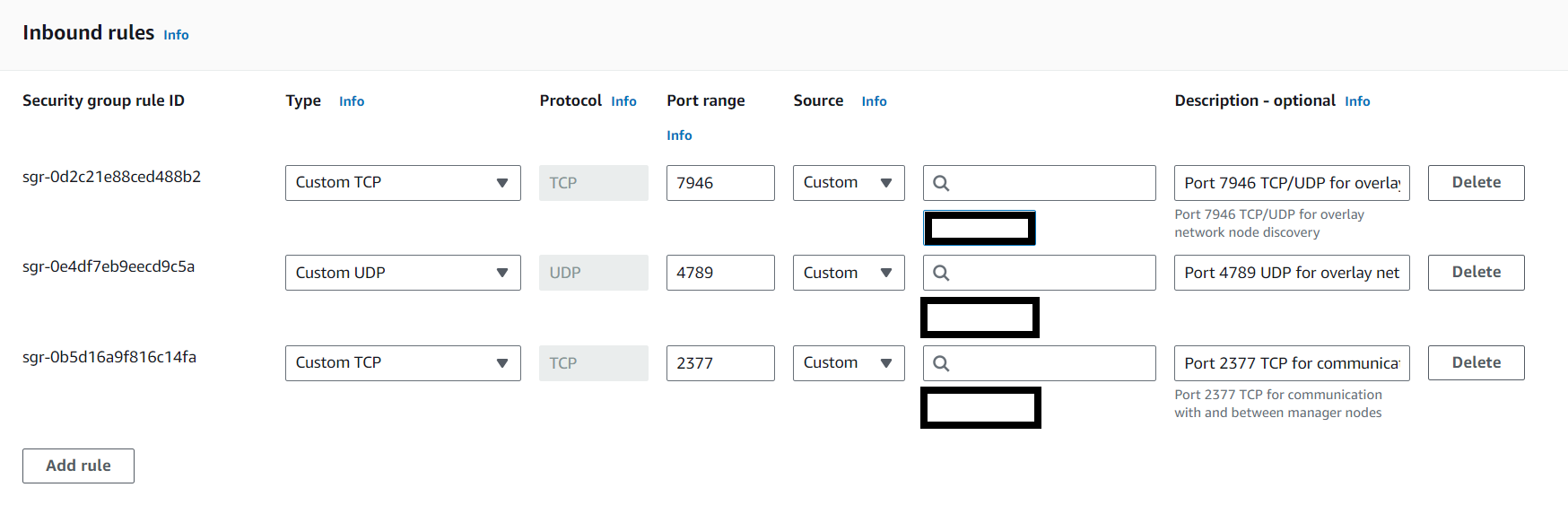
Docker Swarm uses 2377 (for Docker Swarm management), 7946 (for communication among nodes) & 4789 (for overlay network traffic). We will set inbound rules as follows.
Step 2: EC2 instance
We will need two EC2 instances for this cluster, one for Manager node and other for Worker node. While creating EC2 instance, we need to set Security group that we created at the Step 1.
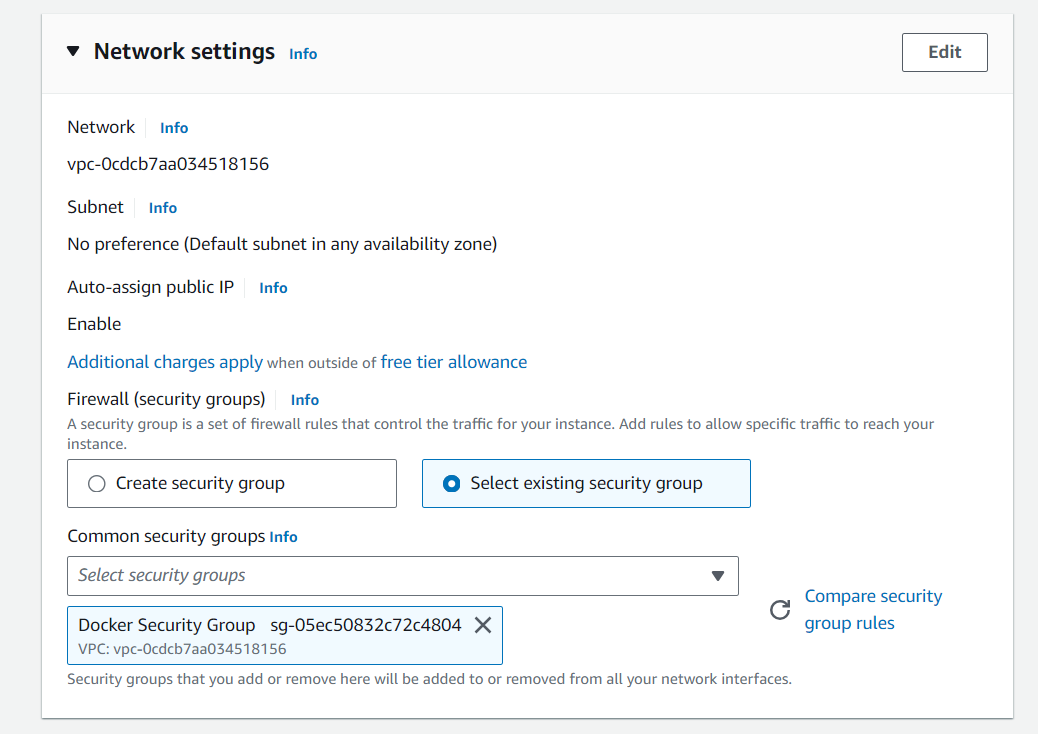
Once the EC2 instances are created we may check the os and architecture. We are using RHEL 9.4 (Plow) with x86_64 architecture for this setup.
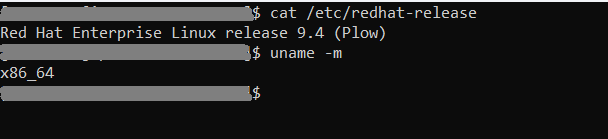
Step 3: Install Docker
Official Docker documentation is well resourced. We may follow the mentioned steps to setup docker.
First we need to uninstall old version if any.
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine \
podman \
runc
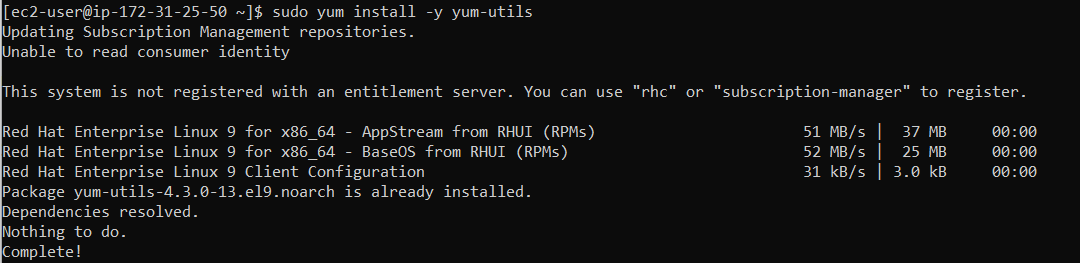
Then we need to install yum-utils package
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
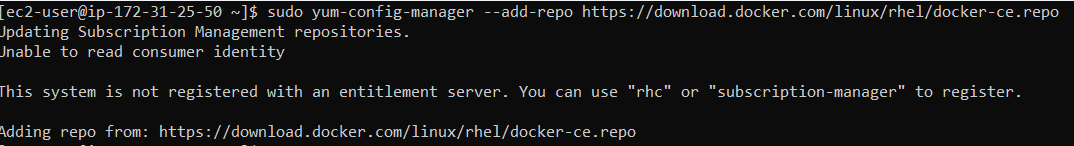
After that we need to set up the REHL Docker repository.
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/rhel/docker-ce.repo
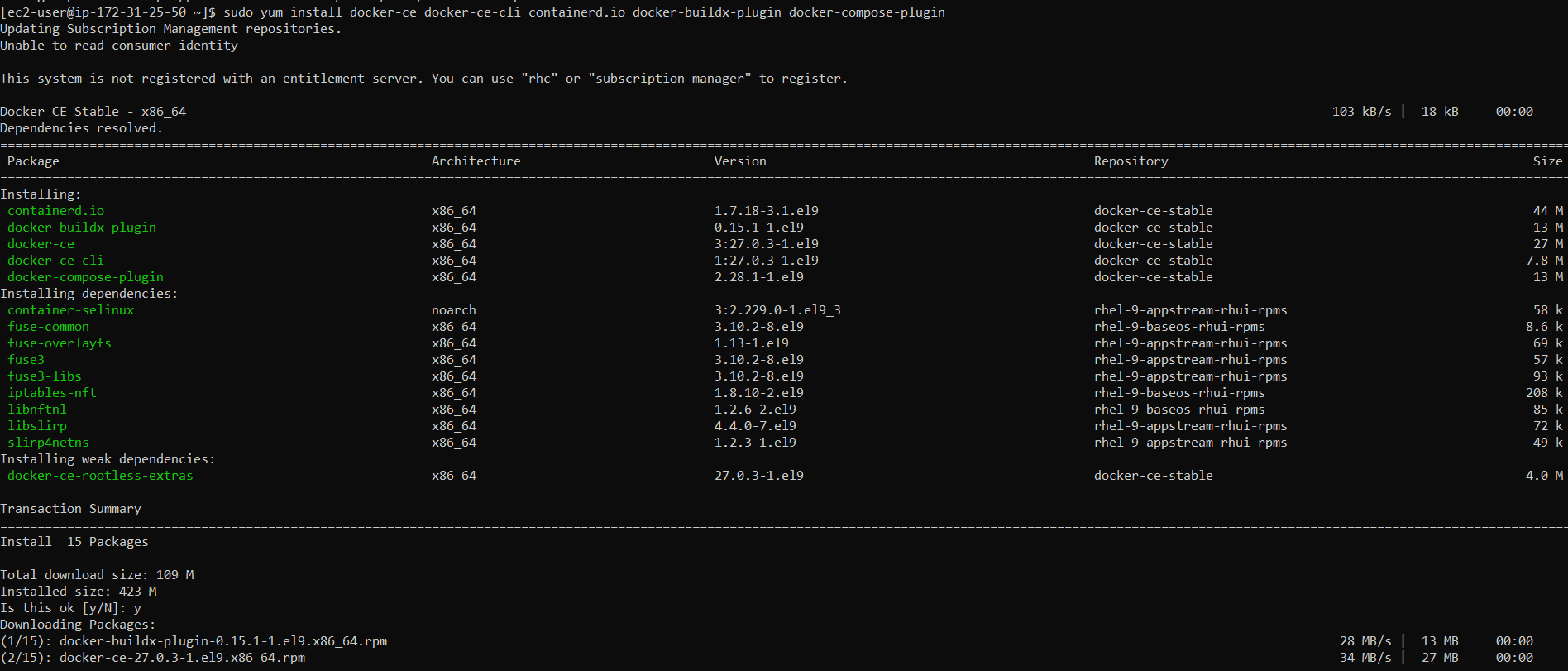
And then install Docker Engine.
sudo yum install docker-ce \
docker-ce-cli \
containerd.io \
docker-buildx-plugin \
docker-compose-plugin
To start docker engine
sudo systemctl start docker
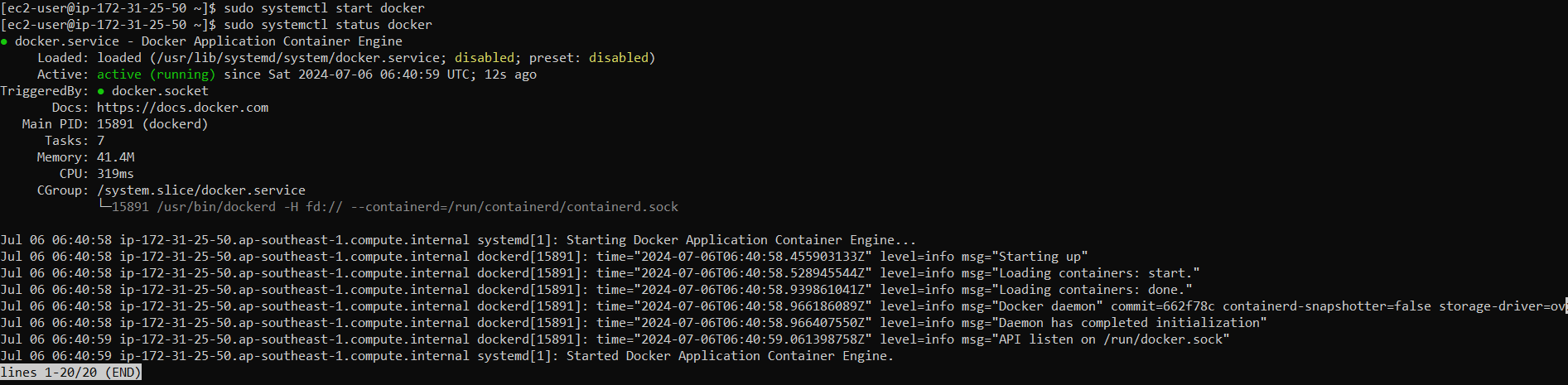
If we want to avoid typing sudo whenever we run the docker command, we need to add username to the docker group.
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
We need to follow Step 3 for both of the EC2 instances (Manager & Worker).
Step 4: Initialize Docker Swarm on Manager node
We need to run the following on the node that we want to be Manager for docker cluster.
docker swarm init
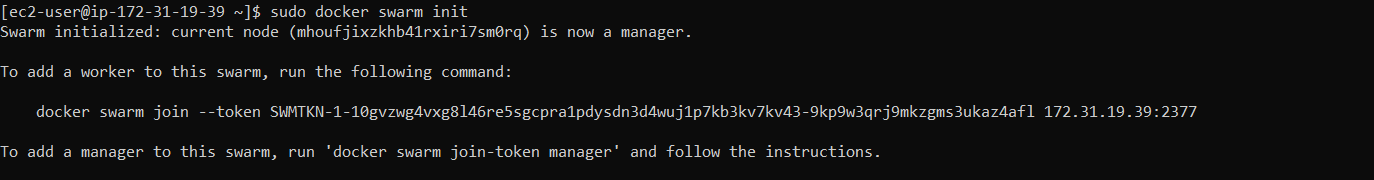
Step 5: Add Worker
We need to copy the output of manager node and run in Worker node to join the cluster.
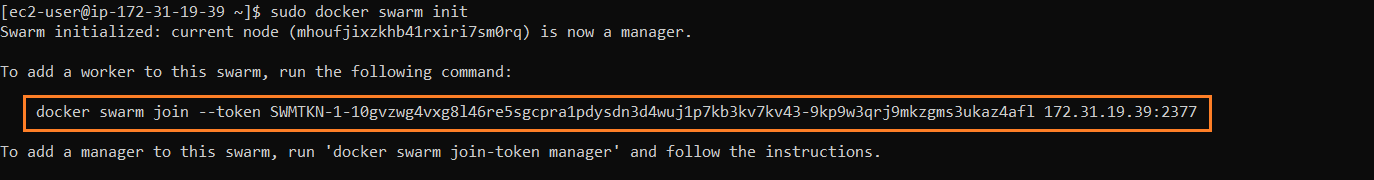
Step 6: Check
Check node status from Manager node. We will see the Manager & Worker node and their status.
sudo docker node ls

Step 7: Run docker stack on cluster
We are using following docker-compose.yml file to run as docker service.
version: '3'
services:
traefik:
image: traefik:v3.0
command:
- --api.insecure=true
- --entrypoints.web.address=:80
- --providers.swarm.endpoint=unix:///var/run/docker.sock
- --providers.swarm.network=dev-network
- --log.level=DEBUG
ports:
- "80:80" # HTTP
- "8080:8080" # Traefik dashboard
networks:
- dev-network
deploy:
placement:
constraints:
- node.role == manager
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
docker-poc-1:
image: limbo93/docker-poc:3
networks:
- dev-network
deploy:
placement:
constraints:
- node.role == manager
ports:
- 8091:8091
docker-poc-2:
image: limbo93/docker-poc:3
networks:
- dev-network
deploy:
placement:
constraints:
- node.role != manager
ports:
- 8093:8091
networks:
dev-network:
driver: overlay
We may run the file as following assuming a service name test.
sudo docker stack deploy -d -c docker-compose.yml test
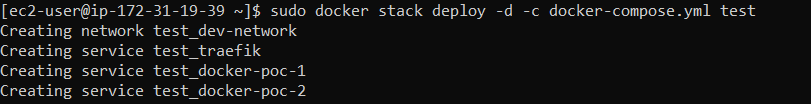
If we check the service status, we will see that the three service is running with prefix of test
sudo docker service ls

If we check from Worker node, we may see that one container is running as described the compose file.

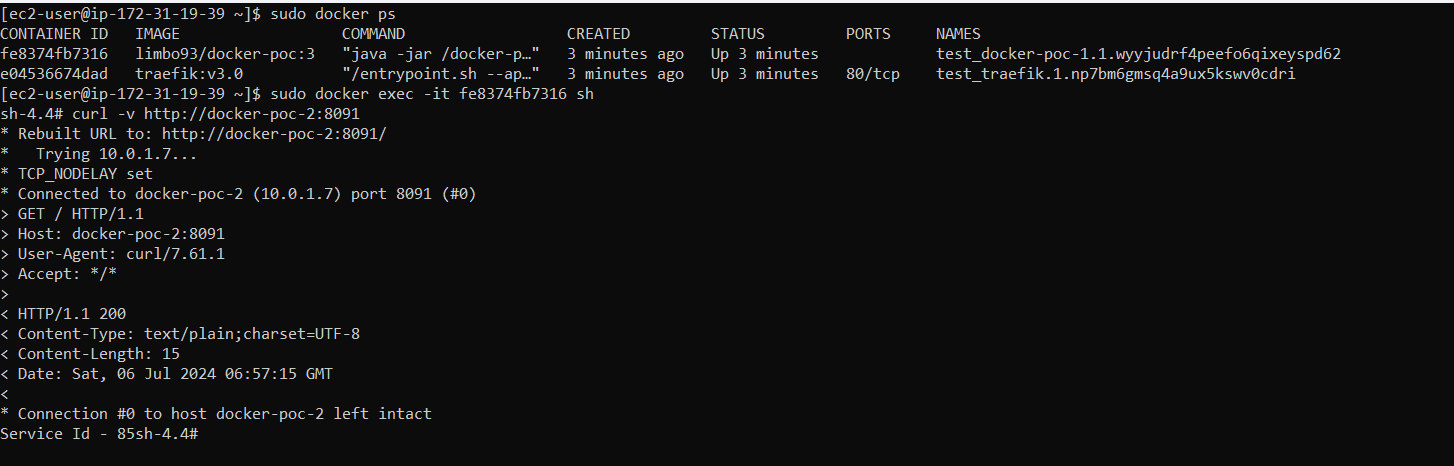
If we check from Manager node, we may see that two container is running as described the compose file. We may also connect a container of Manager node and curl the container of worker node to check the connectivity.
Congratulations! Docker swarm setup with EC2 is complete!